Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM)
Definition
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is a disease that affects the nervous system, specifically the spinal cord, characterized by rapid onset of weakness in one or more limbs and distinct abnormalities of spinal cord gray matter on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can result from a variety of causes.
As of January 1st, 2016 acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) was made a temporarily reportable disease.
Symptoms
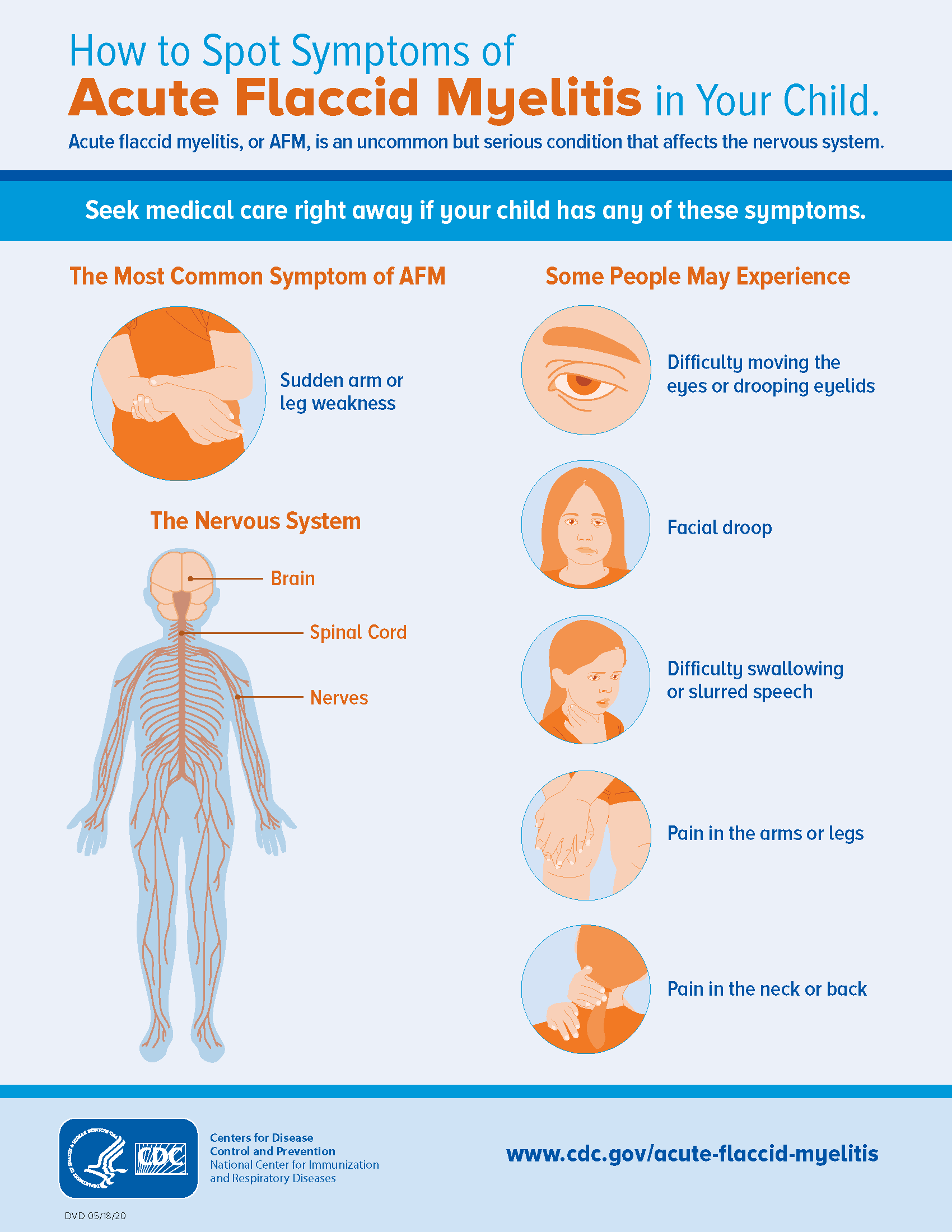
Most patients will have sudden onset of limb weakness and loss of muscle tone and reflexes. In addition to limb weakness, some patients will experience:
- facial droop/weakness
- difficulty moving eyes
- drooping eyelids
- difficulty with swallowing or slurred speech
- numbness or tingling
- pain in arms or legs
- difficulty passing urine
- respiratory failure, if the muscles involved with breathing become weak
Causes
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) may be caused by a variety of agents, including several viruses such as:
- enteroviruses (polio and non-polio)
- West Nile virus (WNV) as well as other arboviruses, specifically Japanese encephalitis virus and Saint Louis encephalitis virus
- herpesviruses, such as cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus
- adenoviruses
Other agents that can cause AFM include:
- environmental toxins
- genetic disorders
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for AFM, but a neurologist may recommend certain interventions on a case-by-case basis.
Prevention
Prevention of acute flaccid myelitis includes many of the same techniques to prevent infections from many viral infections including:
- being up to date on all recommended vaccinations, including poliovirus
- mosquito protection, including repellent and avoidance
- washing your hands often with soap and water
- avoiding close contact with ill people
- cleaning surfaces with disinfectant
Reporting suspected cases of AFM
As of January 1st, 2016 acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) was made a temporarily reportable disease.
Clinicians should report suspected cases (sudden onset of flaccid limb weakness) to Amanda Mandi at (515) 480-5680 or 1-800-362-2736.
Reporting order
Specimen Collection
Clinicians should collect specimens from patients suspected of having AFM as early as possible in the course of illness, preferably on the day of onset of limb weakness, including
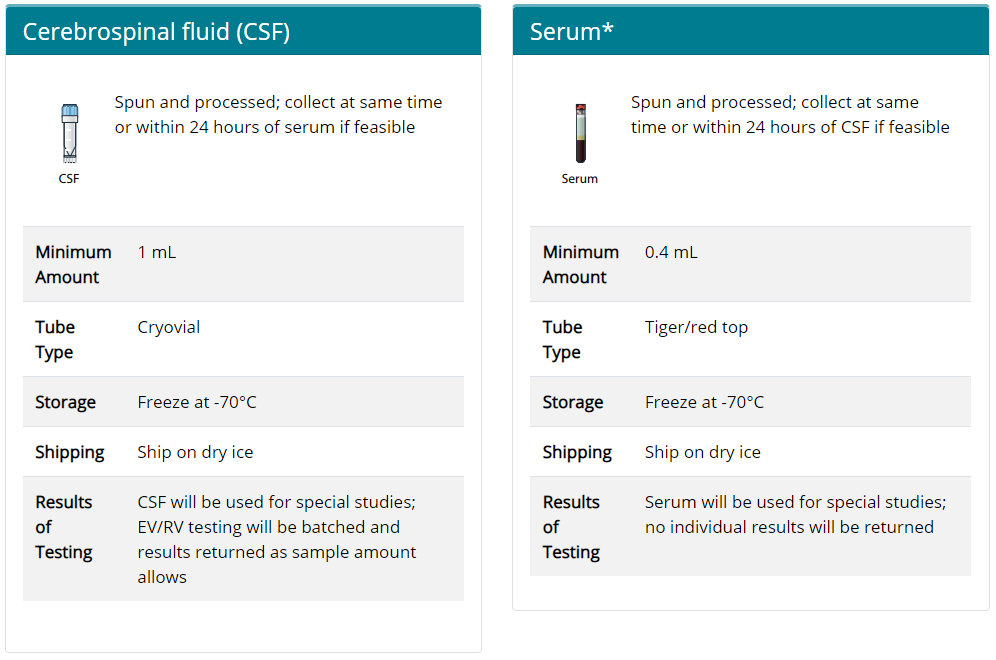
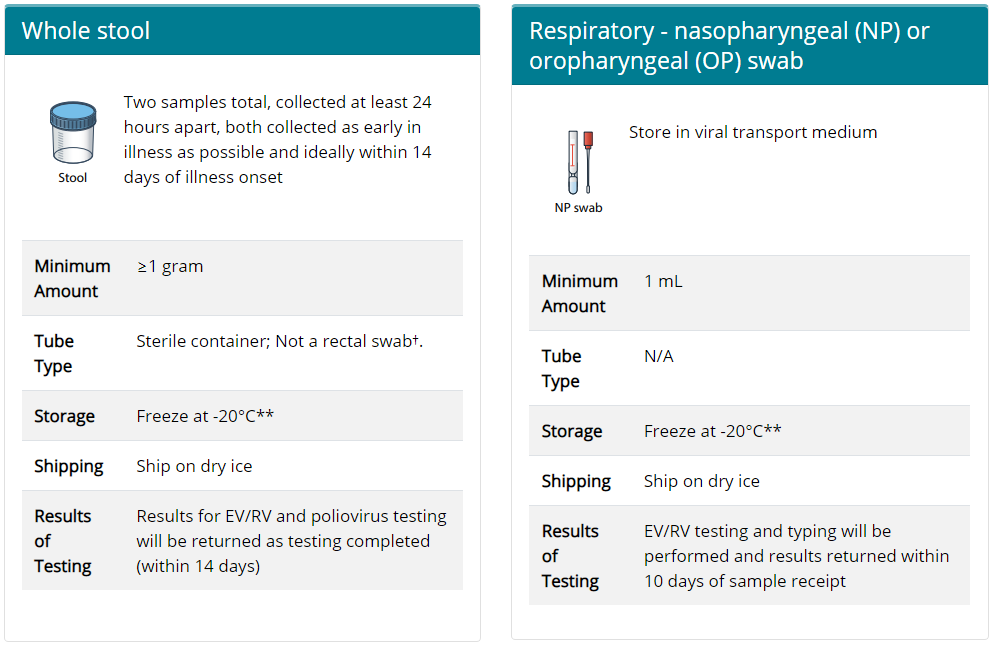
Early specimen collection has the best chance to yield a diagnosis of AFM. Additional instructions regarding specimen collection and shipping can be found at AFM Specimen Collection Instructions.
Call Rob Ramaekers at the Iowa Department of Public Health at (515) 850-8273 or 1-800-362-2736 to arrange specimen shipment to CDC.
Statistics
There have been 673 confirmed cases across the US since CDC began tracking AFM in August of 2014; most of the cases have occurred in children. Two cases of AFM were reported in Iowa in 2018 and one case in 2021.
Additional Resources