Hepatitis A
Definition
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver disease caused by the hepatitis A virus. It is the most common form of viral hepatitis and one of the most frequently reported vaccine preventable diseases in the United States.
Hepatitis A is reportable to the Iowa Department of Public Health by Iowa Administrative Code 641 IAC 1.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hepatitis A usually do not appear until you have had the virus for about a month. Adults are more likely to develop severe symptoms than children. Infected children under three years of age often do not become ill. Initial symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include the following:
- Abrupt onset of fever
- Malaise
- Poor appetite
- Nausea
- Stomach and abdominal pain
After a few days, these symptoms are typically followed by dark (“tea-colored”) urine and jaundice (a yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes). The disease is rarely fatal and most people recover with no complications within one to two weeks, although they may continue to feel tired for a few more weeks.
Infected individuals can spread the virus for one to two weeks before showing any symptoms and for one week after jaundice occurs. Children and infants may occasionally be contagious for longer periods of time.
Causes
Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus and is highly contagious. The virus is found in the feces of infected people and can be spread in several ways:
- When a person with the virus handles food you eat without washing their hands after using the toilet
- Drinking contaminated water
- Being in close contact with an infected person (even if that person does not seem sick)
- Having sex with an infected person
- Eating raw shellfish from water polluted with raw sewage
Risk Factors
Anyone can become infected with hepatitis A but some people are at an increased risk of contracting the disease. Those people include the following:
- People who live in or travel to areas where hepatitis A is common (certain U.S. western states, Central and South America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and the Western Pacific)
- Intimate and household contacts of infected individuals
- Men who have sex with men
- Illegal drug users (injection and non-injection users)
Prevention
A hepatitis A vaccine is available and is recommended for the following persons:
- All children aged 12 to 23 months
- Travelers to areas with increased incidence of hepatitis A
- Men who have sex with men
- Illegal drug users (injection and non-injection users)
- People with blood clotting disorders (e.g., hemophilia)
- People with chronic liver disease (including persons with chronic hepatitis B or chronic hepatitis C infection)
- Residents of a community experiencing an outbreak of hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccine or immune globulin administration is also recommended for close contacts of infected individuals within two weeks of exposure. Close contacts include the following:
- Household contacts
- Sexual contacts
- Playmates
- Attendees at childcare centers
- Persons sharing illegal drugs
- Persons sharing food or beverages
- Persons in common source exposure situations (i.e., co-workers or restaurant patrons where an infected food workers has been identified
The following precautions should also be observed to help prevent the spread of this disease:
- Always wash hands thoroughly with soap and warm water after using the toilet or changing diapers
- Wash children’s hands with soap and warm water after a diaper change
- Teach children to always wash their hands with soap and warm water after using the toilet
- Always wash hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before and after preparing any food
- People with diarrhea should NEVER prepare food for others
Once an infected individual recovers from hepatitis A, they are immune for life and do not continue to carry the virus.
Treatment
Once a person is ill from hepatitis A, there are no special medications available to cure the disease. Bed rest is typically all that is needed. Because this disease affects the liver, infected persons should avoid drinking alcohol and should contact their health care provider before taking drugs or medicines (such as aspirin or Tylenol) since certain drugs must be broken down by the liver. Anyone who suspects they may be infected with this disease should contact their health care provider.
Statistics
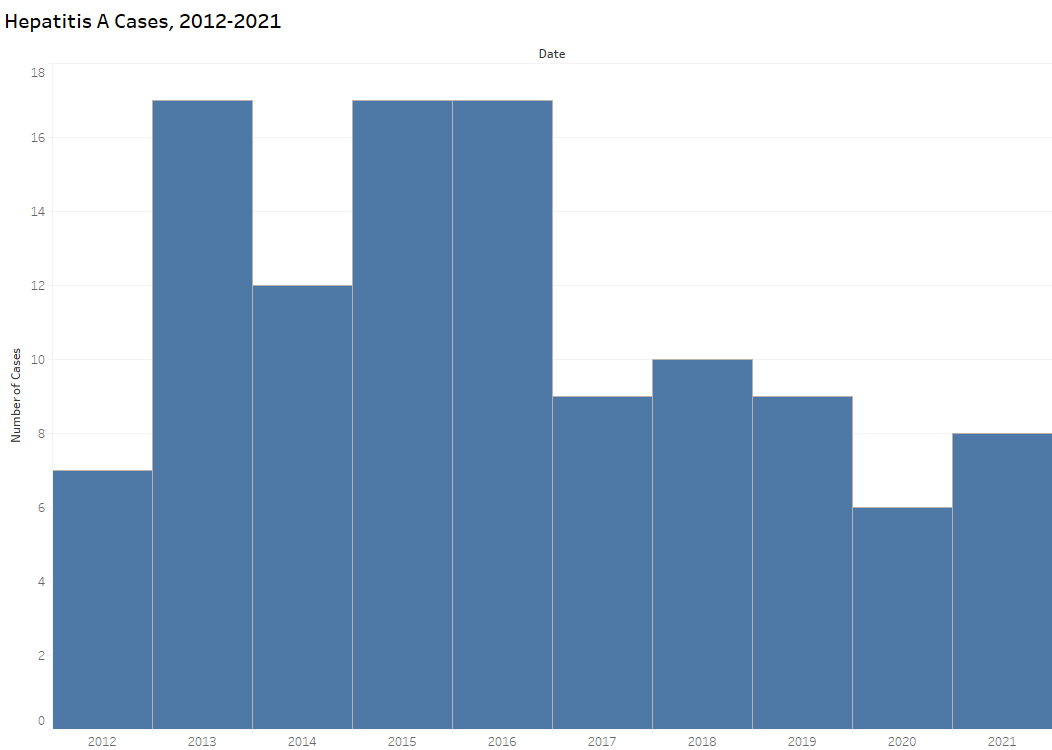
In 2021, 8 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Iowa.
For more detailed information and statistics on all notifiable diseases, please see our current annual report located in the reports section of the CADE homepage.
Additional Resources
Public
Public Health
Schools
Business and Childcare
Health Care Providers