E. coli (shiga-toxin producing)
Definition
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) are bacteria that can cause bloody diarrhea in infected people. In rare cases, the same bacterium can also cause a kidney disease known as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. The most well known member of this group of bacteria is E. coli O157:H7.
Pathogenic E. coli is reportable to the Iowa Department of Public Health by Iowa Administrative Code 641 IAC 1.
Symptoms
Infection may lead to a wide variety of symptoms. Most symptoms start three to four days after exposure to the bacterium. Some people are asymptomatic, whereas others display all of the symptoms listed below. Fever is usually rare, but more common symptoms include:
- Diarrhea (usually bloody)
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Chills
A rare complication that can occur with STEC infection is called Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS). HUS is a kidney disease which can lead to kidney failure and death. This complication is most common in younger children. About 15 percent of children infected with E. coli O157:H7 will develop HUS.
Causes
STEC are members of the species Escherichia coli bacteria. Many E. coli strains are routinely found in the colons of humans and do not cause disease. However, unlike other E. coli strains, STEC produces a toxin called “Shiga toxin.” This toxin is responsible for the bloody diarrhea, HUS, and other symptoms that occur with this infection.
Spread of the bacteria occurs in many ways and includes:
- Drinking water contaminated with human or animal feces containing the bacterium
- Eating undercooked contaminated ground beef or unpasteurized dairy products
- Drinking unpasteurized apple juice, cider, or dairy products
- Eating raw fruits and vegetables that have been contaminated with feces of infected animals
- Person-to-person transmission
Risk Factors
Infection occurs in all age groups, but tends to be diagnosed more in children five years old and younger. This age group is at increased risk of developing HUS and the complications associated with it. Elderly people also appear to be at increased risk for complications.
Prevention
- Do not fix food for other while having diarrhea.
- Wash hands after using the toilet and after changing diapers. Wash the diapered child’s hands also.
- When caring for someone with diarrhea, wash your hands with plenty of soap and water after cleaning the bathroom, helping the person use the toilet, or changing diapers, soiled clothes, or soiled sheets. Be sure to wash their hands also.
- Always refrigerate meat. Never leave raw meat at room temperature
- Cook all ground beef and hamburger thoroughly; to a temperature of 155º F for at least 15-16 seconds or until juices run clear and no pink is visible. Never eat raw meat.
- Always wash hands, cutting boards, and utensils between fixing raw meat or poultry and other items.
- Keep food that will be eaten raw from being in contact food products from animals. Wash these foods thoroughly before eating.
- Drink only pasteurized milk, juice, or cider
- Avoid sexual practices that permit fecal-oral transmission. Latex barrier protection (condoms) should be used to prevent the spread of STEC, as well as other pathogens, to sexual partners.
Treatment
Fluid and electrolyte replacement is the cornerstones of treatment for most STEC infections. Antibiotics have not been shown beneficial, and some may actually be harmful. However, because of the potential for complications, people with suspected STEC infections should be monitored closely. If any signs or symptoms are present that resemble HUS, the patient should be brought to the doctor immediately for observation and treatment.
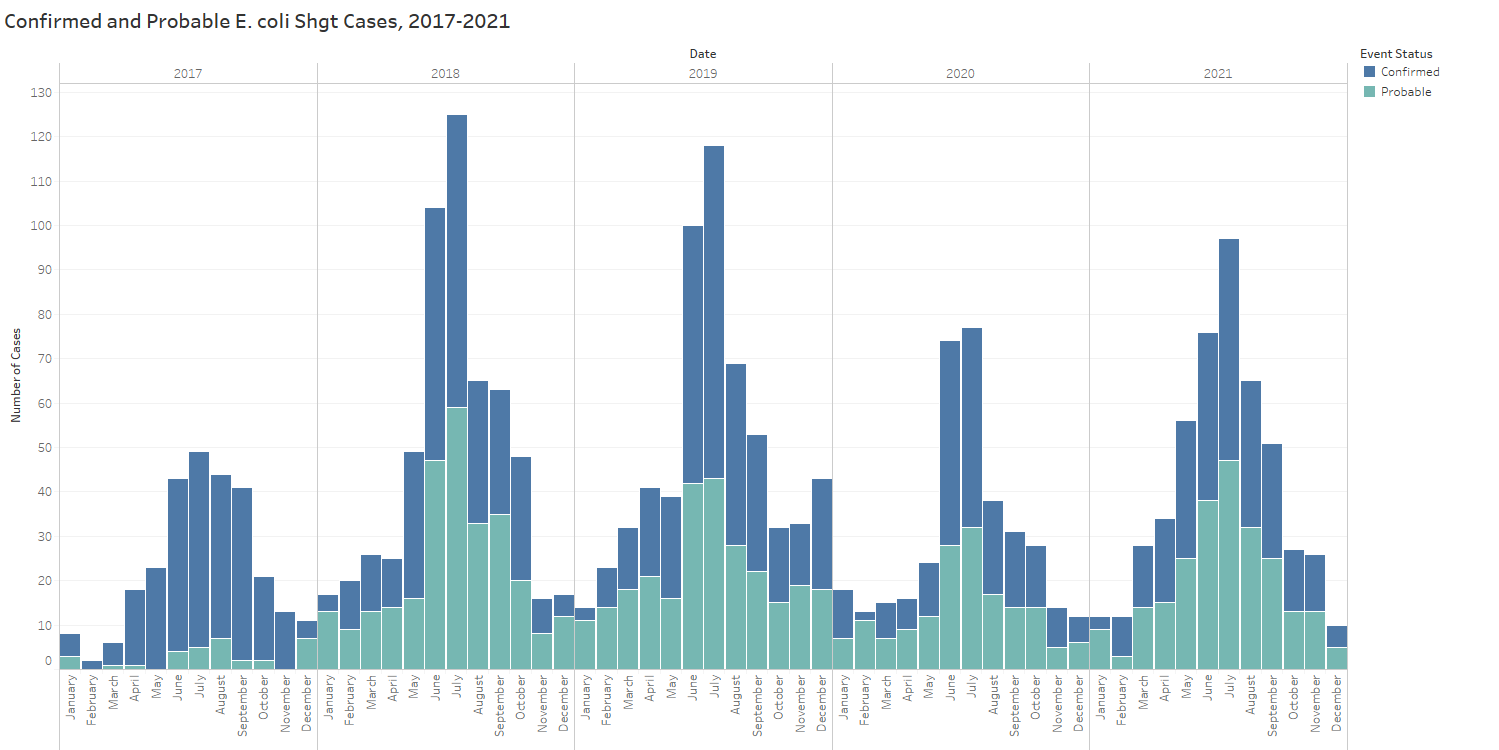
Statistics
There were 494 cases reported in 2021, 15.4 cases per 100,000 population.
For more detailed information and statistics on all notifiable diseases, please see our current annual report located in the reports section of the CADE homepage.
Additional Resources
Public
Public Health
Schools
Business and Childcare
Health Care Providers